Written by JS970
on
on
Greedy Algorithm - Dijkstra Algorithm
Review
- Prim's Algorithm vs Kruskal Algorithm
- Prim's Algorithm Time Complexity : n*n
- Kruskal's Algorithm Time Complexity : m*log m(n-1 <= m <= n(n-1)/2)
- Sparse graph : Kruskal Algorithm
- Kruskal Algorithm(n*log n) is faster than Prim's Algorithm
- Highly connected graph : Prim's Algorithm
- Prim is faster than Kruskal(n*n*log n)
Dijkstra's Algorithm
- 시작 정점 V에서 나머지 정점들까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘이다.
- 알고리즘은 아래와 같이 동작한다.
- Vertex의 부분집합 Y(처음에는 시작 정점만 포함된다. 선택된 정점을 의미한다.)
- V는 모든 정점의 집합을 의미한다.(G = (V, E), 선택되지 않은 정점을 의미한다.)
- F는 edge집합의 부분집합이며, 시작 정점에서 다른 노드로의 최단 경로에 사용되는 edge의 집합이다.
- V-Y에 속한 vertex중 시작 정점과 가장 가까운(weight이 가장 작은) vertex를 선택한다. 과정에서 Y집합에 포함된 vertex는 중간 노드(intermediate node)로 활용할 수 있다.
- 선택된 vertex를 집합 Y에 추가한다.
- 선택된 vertex가 destination node인 edge를 F에 추가한다.
- Y=V일때까지(모든 정점에 대한 최단거리를 구할 때까지) 4~6을 반복한다.
- Prim Algorithm과 유사하다.
한 정점에서다른 정점까지의 최단 경로를 구한다.(이 부분이 Prim과 다르다.)Prim은MST를 구하는 것이 목적이다.Dijkstra는 MST가 아닌최단 경로를 구하는 것이 목적이다.- Prim의 MST가 Dijkstra의 최단 경로를 보장하지 않으며, 역 역시 마찬가지이다.
모든 정점에서 다른모든 정점으로의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘으로는Floyd's all-pair Algorithm이 있다.- 아래는 Dijkstra's Algorithm이 적용되는 과정을 나타낸 도식이다.
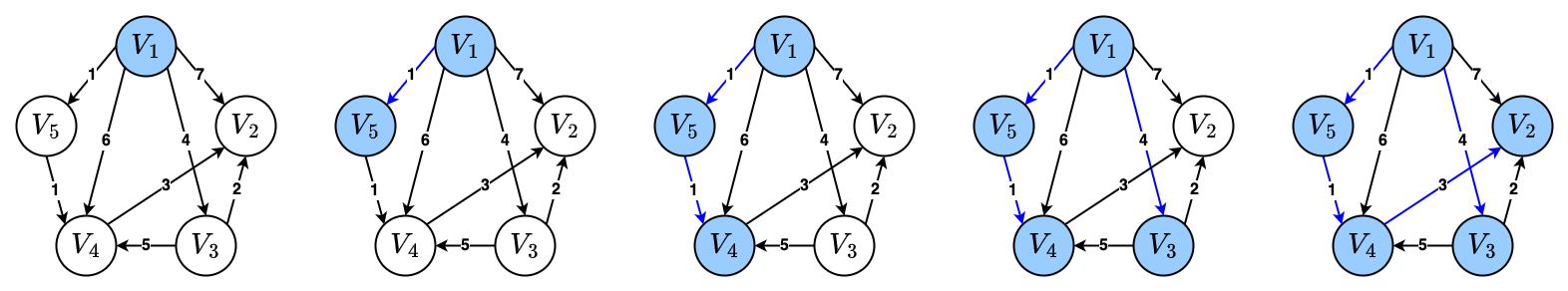
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
// (가중치, 노드)값을 나타내는 상수
typedef pair<int, int> pil;
void dijkstra(vector<vector<pil> >& graph, int start, vector<int>& distance) {
// 시작 노드의 거리를 0으로 초기화
distance[start] = 0;
// min heap을 사용하는 우선순위 큐
priority_queue<pil, vector<pil>, greater<pil> > pq;
// 시작 노드의 가중치는 0으로 설정
pq.push(make_pair(0, start));
while(!pq.empty()) {
// 현재 선택된 노드
int curr_node = pq.top().second;
// 현재 노드까지의 거리(가중치 값으로 초기화)
int curr_dist = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
// 이미 처리한 노드면 건너뛴다.
if(curr_dist > distance[curr_node]) continue;
// 현재 노드와 연결된 인접 노드를 탐색한다.
for(int i = 0; i < graph[curr_node].size(); ++i) {
// 다음 노드
int next_node = graph[curr_node][i].second;
// 다음 노드까지의 거리
int next_dist = curr_dist + graph[curr_node][i].first;
// 다음 노드까지의 거리가 현재 기록된 거리보다 짧다면 갱신 후 큐에 삽입한다.
if(next_dist < distance[next_node]) {
distance[next_node] = next_dist;
pq.push(make_pair(next_dist, next_node));
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n = 5; // 노드의 개수
int start_node = 1; // 시작 노드
// 그래프 초기화
vector<vector<pil> > graph(n + 1); // 인덱스를 1부터 사용하기 위해 크기를 n+1로 설정
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(7, 2));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(4, 3));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(6, 4));
graph[1].push_back(make_pair(1, 5));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(2, 2));
graph[3].push_back(make_pair(5, 4));
graph[4].push_back(make_pair(3, 2));
graph[5].push_back(make_pair(1, 4));
// 최단 거리를 저장하는 배열 초기화
vector<int> distance(n + 1, INT_MAX);
// 다익스트라 알고리즘 호출
dijkstra(graph, start_node, distance);
// 결과 출력
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (distance[i] == INT_MAX)
cout << "INF ";
else
cout << "1 -> " << i << " : " << distance[i] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- 출력 결과

Every-case Time Complexity of Dijkstra Algorithm
- The number of vertices : n
- Basic Operation : n-1회의 while loop(시작정점을 제외한 모든 정점에 대해 탐색한다.)
- 각 loop내부에서 n-1회 순회하며 각 단계의 정점의 모든 edge에 대한 minimum distance를 찾는 연산을 수행한다. $$T(n) = (n-1)\times (n-1) \in \Theta(n^2)$$